Lack of amino acids can lead to depression
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Multiple amino acids linked together are called peptides and multiple peptides linked together are the polypeptides/proteins or otherwise called proteins. Hormones and neurotransmitters can also consist also of amino acids. Each protein has a different sequence and amount of certain amino acids. Although depression is often a mix of complex factors, a lack of certain amino acids can potentially contribute to depression. The amino acids most often then on the low side are those involved in forming serotonin and dopamine:
Tryptophan: Tryptophan is an essential amino acid required for the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter involved in mood and sleep. A deficiency in tryptophan can potentially lead to decreased serotonin production and disturbed mood.
Tyrosine: Tyrosine is a precursor of dopamine, norepinephrine and adrenaline. These neurotransmitters play a role in motivation, reward and energy levels. Tyrosine deficiency can potentially lead to decreased production of these neurotransmitters, which can contribute to symptoms of depression.
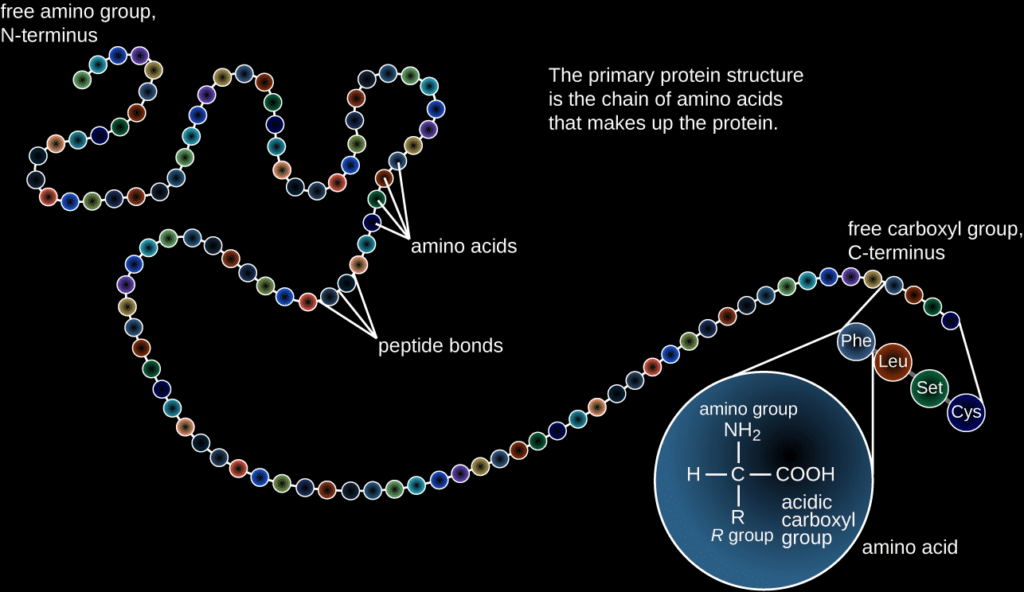
What amino acids are there?
In nature, there are about 500 different amino acids. The human body basically uses only 20, which we call fundamental amino acids. Of those 20, we can make 11 from other amino acids or we recycle the amino acids we get from food. The other 9 amino acids we really need to get through food and we call them essential amino acids.
Herewith a list of fundamental amino acids
| Name | 3-Letter Symbol | 1-Letter Symbol | Molecular Formula |
| Alanine | Ala | A | C3H7NO2 |
| Arginine** | Arg | R | C6H14N4O2 |
| Asparagine | Asn | N | C4H8N2O3 |
| Aspartic acid | Asp | D | C4H7NO4 |
| Cysteine** | Cys | C | C3H7NO2S |
| Glutamic acid | Glu | E | C5H9NO4 |
| Glutamine | Gln | Q | C5H10N2O3 |
| Glycine** | Gly | G | C2H5NO2 |
| Histidine* | His | H | C6H9N3O2 |
| Hydroxyproline | Hyp | O | C5H9NO3 |
| Isoleucine* | Ile | I | C6H13NO2 |
| Leucine* | Leu | L | C6H13NO2 |
| Lysine* | Lys | K | C6H14N2O2 |
| Methionine* | With | M | C5H11NO2S |
| Phenylalanine* | Phe | F | C9H11NO2 |
| Proline | Pro | P | C5H9NO2 |
| Pyroglutamatic | Glp | U | C5H7NO3 |
| Serine | Ser | S | C3H7NO3 |
| Threonine* | Thr | T | C4H9NO3 |
| Tryptophan* | Trp | W | C11H12N2O2 |
| Tyrosine** | Tyr | Y | C9H11NO3 |
| Valine* | Val | V | C5H11NO2 |
*Essential amino acid
**Semi essential amino acid
What does a healthy body need?
A healthy body is never deficient in the amino acids that the healthy body needs to function. In general, people generally do get enough non-essential amino acids. Therefore, it is often the essential amino acids that a person is deficient in because they cannot be made from other amino acids when deficient.
Protein requirement per day
In order to meet our daily protein requirements and thus amino acids, we actually need to have some protein in every meal to ultimately meet our needs. An adult with a normal exercise level needs about 1 gram of net protein per kilogram of body weight per day. So if someone weighs 75kg, he or she should eat 75 grams of protein containing the right amino acids.
Some people need more protein
- Top athletes and especially in strength training
- People who practice heavy physical work
- COPD patients
- People with serious illnesses
- People in recovery/operation
- Pregnant women and breastfeeding women
- Growing children
- To lose weight
Not all proteins contain the right proportions of amino acids
The body can most optimally utilize a protein from food if it best matches the amino acid profile of the human body. These are proteins that are very close in structure and ratio of essential amino acids to those of the body’s own proteins. The more amino acids present, the better. So the essential amino acids must come in through the diet to eventually make all 20 amino acids our body needs.
How high quality a protein-rich food is is indicated by the term Biological Value of proteins. Animal proteins generally have a higher Biological Value than vegetable proteins, because animal proteins regarding structure and amino acids used are more similar to our own proteins. Therefore, it is even more important for vegetarians to eat proteins (or combinations of proteins) that result in a high Biological Value!
Protein/Biological value
| Whey isolate | 140 |
| Whey concentrate | 120 |
| Breast Milk | 100 |
| Egg white | 100 |
| Egg (whole) | 94 |
| Cheese | 84 |
| Chicken | 79 |
| Turkey | 79 |
| Casein (milk protein) | 77 |
| Soy | 74 |
| Fish | 70 |
| Lean meat | 69 |
| (Cow) milk | 60 |
| Unprocessed rice | 59 |
| Brown rice | 57 |
| White rice | 56 |
| Peanuts | 55 |
| Peas | 55 |
| Wheat | 49 |
| Soybeans | 47 |
| Flower | 41 |
| Corn | 36 |
| Brown beans | 34 |
| Potatoes | 34 |
Foods you can combine
If different protein sources are eaten together, the amino acids that are deficient in one product may be replenished by the other. Some well-known combinations include.
| Product | Combine with |
| Grain products | Legumes, acidified dairy, meat, fish, cheese or egg |
| Vegetable | Oats, rye, egg or sesame seeds |
| Potatoes | Egg, Wheat or acidified dairy products |
So it is advisable to alternate foods in order to get the right amino acids. Keep in mind that some foods score well on protein content and less so in other areas. Nowadays it is easier and more beneficial for the body to buy a jar of essential amino acids and BCAA and eat a healthy diet. This way you get the good things without the disadvantage of some animal products.

A word about protein preparations
If you really want to be sure you are getting the right amino acids and in the right amount, there are a few supplements such as protein powders that are recommended.
Whey hydrolisate is a pre-digested milk protein with high absorbability and high bioavailability of 140. For athletes and people with increased protein needs, this protein is ideal for getting the right amino acids in high amounts.
Pepto Pro is pre-digested casein protein which is divided into peptides and these are even more absorbable, but the biological value is slightly lower than Whey.
Silverback Protein is a plant-based pea protein supplemented with additional essential amino acids so it has as good a biological value as Whey, but plant-based and lactose-free.
Essential amino acid mix is a mix of amino acids to supplement the protein from your diet without actually adding extra protein. This option is especially useful for when you think you are eating enough protein but not the right amino acids. Some manufacturers also add glutamine and BCAA to the essential amino acids, which is our preferred option. You can also add them yourself (via nutrition).
Attention to these essential amino acids
Lysine, involved in concentration ability, calcium absorption, bone tissue growth, collagen building and immune system support, especially with susceptibility to viral infections such as cold sores, it is important to have ample lysine in your diet .
Sources: fish, meat, egg, dairy such as cottage cheese, ricotta, yogurt, avocado, nuts & seeds, legumes, seafood, brewer’s yeast, beans, wheat germ, legumes, bean sprouts.
Tryptophan, involved in resistance, stress management, good sleep, pain, constipation and depression.
Sources : egg, bananas, milk, rice, cottage cheese, meat, oats, nuts, lentils, seeds, legumes.
Leucine, involved in growth/repair of muscle tissue, wound and bone healing, sugar metabolism.
Sources : egg, rye, lima beans, almonds, cashews, dairy, rice, chickpeas, beef, chicken, fish, seafood, whole wheat, almonds, cashews, lentils, beans.
Valine, growth and repair of muscle tissue, nervous system function, addictions and in people with constant feelings of hunger.
Sources : egg, brown rice, cottage cheese, meat, lima beans, mushrooms, almonds, cashews, peanuts, sesame seeds, lentils, mushrooms, soybeans.
Isoleucine, involved in building and growth of muscle tissue and energy production at the cellular level.
Sources : egg, meat, dairy, seafood, beans, rye, almonds, cashews, chickpeas, sunflower seeds.
Methionine, involved in skin/hair/nails health, countering fat deposits in the body, liver detoxification, histamine breakdown and as an antioxidant.
Sources: egg, meat, sardines, eggs, oats, bean sprouts, nuts, avocado, seeds, dairy products, fish, seafood, wheat germ, oat flakes, nuts, sesame seeds, lentils, soybeans, avocado.
Threonine, involved in brain metabolism, digestion and production of collagen and tooth enamel.
Sources: Egg, fish, meat, almonds, peanuts, beans, dairy products, meat, fish, seafood, wheat germ, oat flakes, nuts, legumes.
Phenylalanine, especially important for people with a lot of stress/pain/depression and obesity.
Sources: dairy products, meat, poultry, fish, seafood, wheat germ, oat flakes, nuts, lentils, soybeans.
Histidine, especially in children who grow quickly or people with a lot of anxiety.
Sources: white of egg, meat, poultry, wheat germ, peanuts, sesame seeds.
Not essential yet often lacking
Glutamine, is not essential but can be essential in cases such as leaky gut, addiction sensitivity or ammonia-scented sweat. Glutamine deficiencies can lead to all kinds of allergies and intolerances like cow’s milk, soy, nuts, peanuts but also to deficiencies of GABA, our body’s own “tranquilizer.
Sources of glutamine: liver, dairy products, cabbage, cottage cheese, ricotta cheese, avocado, wheat germ, whey.
Arginine, is not essential but can be very essential in (wound) healing, high blood pressure, fertility problems, athletes or slow regeneration after exercise.
Sources: cheese, meat, poultry, eggs, fish, shellfish, nuts&seeds (especially walnuts, peanuts, pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds/Tahini, macadamia, hazelnuts and almonds),buckwheat, chocolate, peas, avocado, soy, garlic, ginseng.
Tyrosine, especially in depression, liver, thyroid and/or adrenal disorders very essential.
Sources: herring, avocado, meat, almonds, sesame seeds, chickpeas, pecans.
Specific amino acids against depression, compulsions, addictions and inflammatory diseases
There are a number of forms of amino acids that have been proven to be very effective against certain conditions. These specific forms of amino acids often have an extra atom (group) to the molecule so they get to certain places in the body better. Below are the specific forms of amino acids that work extra well.
N-acetyl cysteine
N-acetyl cysteine works against addictions, premature aging, inflammatory diseases, depression, compulsive acting (OCD), stress and also increases fertility in men and women. N-acetyl cysteine can help fight:
- Mucus in airways and/or sinuses, respiratory diseases (respiratory infections, emphysema, chronic bronchitis, cystic fibrosis, asthma, sinusitis, hay fever, pulmonary fibrosis)
- Chronic liver diseases
- Aging
- HIV/AIDS (improving glutathione status)
- Immunosenescence in the elderly (aging immune system with consequent decreased resistance and chronic low-grade inflammation)
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Sports (better endurance, faster recovery)
- Addictions (smoking, gambling, cannabis, cocaine, methamphetamine, heroin)
- OCS (obsessive-compulsive disorder)
- Sjögren’s disease (eye complaints)
- Sickle Cell Disease
- Cancer (prevention)
- Diabetes mellitus (improve glycemic control, prevent complications including thrombosis)
- Pancreatitis
- Kidney diseases
- PCOS (polycystic ovarian syndrome)
- Endometriosis
- Infection with Helicobacter pylori (causative agent of peptic ulcer, stomach cancer)
- Arthritis
- Crohn’s disease
- Autism
Depression, bipolar disorder (depressive phase) - Schizophrenia
- Brain injury, spinal cord injury, stroke
- Prevention of noise-related deafness
N-acetyl cysteine is not found in our diet, but the body makes it from L- cysteine. In many cases of the pathologies described above, too little N-acetyl cysteine is made from L- cysteine and then supplementation is a solution.
The daily dosage of N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) is 1000 mg and as a therapeutic daily dose is approximately 2000 mg. Ingestion is best taken on an empty stomach with water.
Caution with medications. N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) may increase the effects of antidepressants, nitroglycerin and anticoagulants. Consult your doctor first if you are taking any medications.
Acetyl-L-carnitine
Acetyl-L-carnitine works particularly well against depression and inflammatory diseases. Acetyl-L-carnitine (ALCAR) increases the synthesis of serotonin (low serotonin actually causes depression) and it makes the mitochondria, the energy factories in cells, work better so that it prevents depression from exhaustion. Acetyl-L-carnitine can help with the following disease states:
- Aging (decreased endogenous carnitine synthesis)
- Low carnitine intake with diet (vegetarianism, veganism)
- Chronic fatigue (including cancer, multiple sclerosis, celiac disease, old age, chronic fatigue syndrome, hepatitis C, beta-thalassemia)
- Depression in the elderly
- Age-related cognitive decline, dementia
- Cardiovascular diseases (intermittent claudication, angina, myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, myocarditis, premature ventricular contractions, cardiomyopathy, hypertension, stroke, Raynaud’s disease)
- Diabetes mellitus, obesity, metabolic syndrome
Neuropathy (diabetes, chemotherapy, HIV medication) - Age-related macular degeneration
- Reduced fertility
- Fibromyalgia
- Cancer Cachexia
- Hyperthyroidism (not hypothyroidism!)
- Sports (improving endurance)
- COPD (for increasing exercise capacity)
- Hepatic encephalopathy, liver cirrhosis
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver and steatohepatitis
- Renal failure/kidney dialysis
- HIV infection
The recommended dosage is 1 to 3 grams per day and on an empty stomach preferably not in the evening.
Caution with medications. Acetyl-L-carnitine (ALCAR) may increase the effects of antidepressants, nitroglycerin and anticoagulants. Consult your physician first if you are taking any medication.
Nutrition and physical health is part of Trip Therapy
A healthy body gives a greater chance of a healthy mental state and vice versa. Psychedelic therapy combined with a healthy lifestyle significantly increases the chance of fighting the symptoms of mental symptoms. Here are some reasons why this combined approach can give a chance of positive results:
- Neuropsychological effects: Psychedelics, such as psilocybin (in magic mushrooms) and lysergic acid di-ethylamide (LSD), have potentially therapeutic effects on the brain. They can enhance communication between different brain regions and make new connections, which can lead to increased insight, introspection and emotional well-being. These effects can address mental symptoms and help the person develop new perspectives.
- Emotional processing: Psychedelic therapy can trigger deep and intense emotional experiences. This can enable people to recognize and cope with ingrained patterns, negative thoughts and traumatic memories. It can help reframe experiences and promote emotional processing, which in turn can lead to relief from mental symptoms.
- Increase self-insight and introspection: Psychedelic experiences can induce a sense of connection and oneness with the self, others and nature. This can increase self-insight and promote a deeper understanding of one’s own mental state. Through this introspection, people can become aware of underlying causes of their mental symptoms, such as unprocessed traumas, negative beliefs or destructive behavior patterns.
- Strengthening therapeutic processes: In a therapeutic setting, psychedelics can enhance the effectiveness of other therapeutic approaches. It can facilitate communication with therapists, break down barriers and speed up therapeutic processes. Psychedelic therapy can also increase overall acceptance of therapy, making people more open to change and growth.
- Healthy lifestyle to complement: A healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition, exercise, adequate sleep and stress management, can promote overall mental health and well-being. By embracing a healthy lifestyle, people can increase their physical and mental resilience, which can contribute to the success of psychedelic therapy. In addition, a healthy lifestyle can help support long-term positive changes and prevent relapse.
Take advantage of our complete approach
At Trip Therapy, completing the intake is the first step you can take to qualify for psychedelic therapy including advice on physical health. Through the intake we can estimate if certain neurotransmitters are too low and what foods and supplements you can use to improve neurochemistry. Improving neurochemistry beforehand has a number of advantages such as a better psychedelic session with less risk of a negative experience such as a bad trip. Furthermore, improving neurochemistry can already mean a better state of mind. Take the first step and fill out the intake:
